了解 Solana架构
在本模块中,我们将深入剖析Solana的复杂架构,重点关注其革命性的历史证明(PoH)共识机制,以及它如何与权益证明(PoS)协同实现无与伦比的交易速度。我们将深入研究提升Solana可扩展性和效率的关键组件,如Sealevel、Gulf Stream和Turbine。通过对这些功能的详细探索,学习者将更深入地了解使Solana能够以光速处理交易的技术创新。
权益证明 (PoS) and 历史证明 (PoH) 共识机制

Solana采用权益证明(PoS)共识机制,这是比特币等网络采用的高能耗工作证明(PoW)的常见替代方案。在PoS中,验证者根据持有的代币数量和愿意“押注”的代币数量来选择创建新区块和确认交易的验证者。这种机制提升了网络的安全性和能效性。
历史证明(PoH)是Solana中PoS系统的补充,这一独特功能有助于网络实现高吞吐量和低延迟。PoH的工作原理是创建历史记录,证明事件发生在特定时间点,为交易过程增加了一层时间验证。PoS和PoH的结合使Solana能够快速高效地处理交易,大大减少了确认交易所需的时间和计算能力。这种效率是Solana能够每秒处理数千笔交易(TPS)的关键因素。这种奖励机制鼓励更多用户将代币投入其中,进而提高了网络的安全性和稳定性。
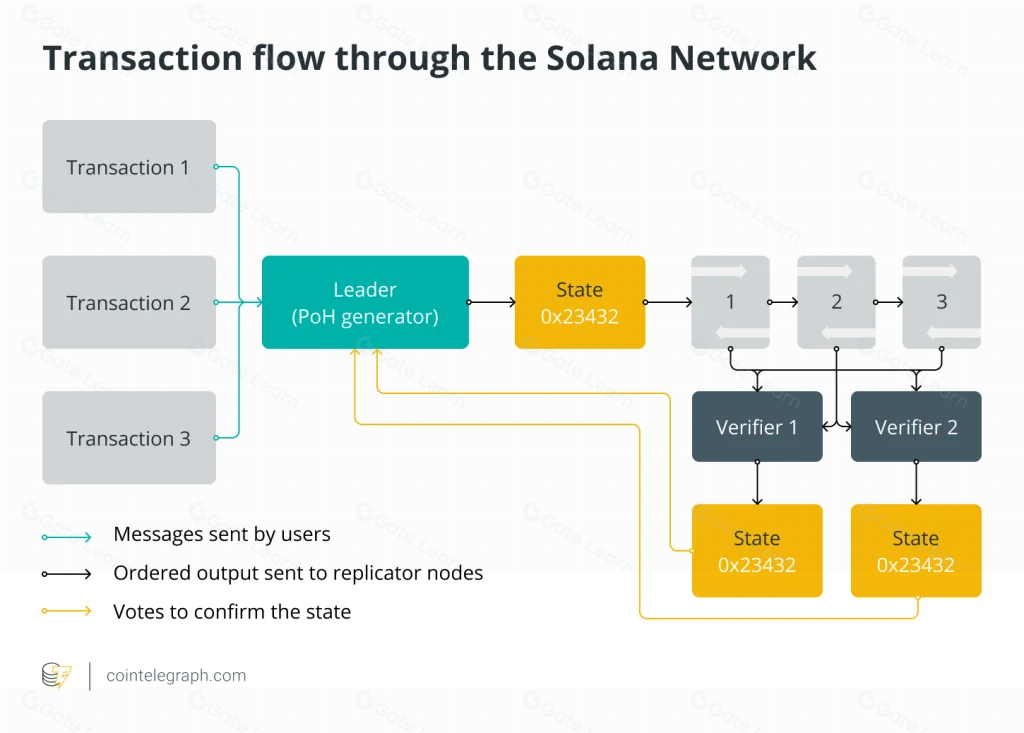
Solana 实施 PoS代表了区块链技术的重大进步,为传统 PoW 系统提供了一种可扩展且环保的替代方案。它是 Solana 架构的基石,使网络得以快速发展和采用。
独特功能: Gulf Stream, Sealevel, Tower BFT, Turbine
Gulf Stream

Gulf Stream是Solana的内存池管理系统,在其高性能区块链基础设施中发挥着至关重要的作用。与传统系统中交易在内存池中等待验证者将其纳入区块的方式不同,Gulf Stream甚至在当前区块最终确定之前就将交易推送给验证者。这种预见性方法允许验证者提前准备和执行交易,大大缩短了确认时间,提高了网络的整体效率。
该机制使Solana能够支持高吞吐量的交易,每秒可处理数千笔交易,而不会造成网络拥塞。通过最大限度地减少对Mempool的依赖,Gulf Stream降低了网络拥塞的风险和相关费用,确保了更流畅、更可预测的交易体验。在使用高峰期,传统的区块链网络可能会因交易量增加和处理时间延迟而陷入困境,而这一功能尤其有益。
通过确保交易提前分配给验证者,该系统即使在重载情况下也能保持高性能,使其成为对需要快速高效区块链服务的开发者和用户极具吸引力的平台。
Sealevel

Sealevel是Solana独有的并行智能合约运行时,能够同时处理数千份智能合约。这一功能是Solana可扩展性的基础,使其能够实现无与伦比的交易速度和吞吐量。通过并行执行智能合约,Sealevel充分利用网络的计算资源,避免了在顺序处理环境中可能出现的瓶颈。
Sealevel的架构设计能够自动识别非重叠交易,这些交易可以安全地并行处理,不会发生冲突。这确保了区块链的完整性和状态得以保持,即使在同时处理大量交易时也是如此。该系统能够利用额外的计算资源进行横向扩展,因此非常适合需要高性能和快速响应时间的复杂应用。
Sealevel的并行处理能力扩展了Solana上去中心化应用(dApps)的潜力,可支持比其他区块链更复杂和资源密集型的应用。
Tower BFT

Tower BFT是Solana为 Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) 共识机制定制的版本,在性能和安全性方面进行了优化。它集成了历史证明(PoH)组件,为区块链添加了独特的计时机制。这种集成允许验证者在减少通信开销的情况下就事件顺序和区块链状态达成一致,从而提高了网络的效率和可扩展性。
Tower BFT中PoH的创新使用使Solana能够在不影响去中心化或安全性的情况下更快地达成共识。通过提供可验证的事件序列,Tower BFT允许网络比基于BFT的传统区块链更迅速地处理和完成交易。这对于保持Solana的高吞吐量和低延迟交易处理能力至关重要。
Turbine

Turbine是Solana中的一个区块传播协议,旨在解决在网络中广播大型区块时面临的挑战。通过将数据分解成更小的数据包,Turbine能够高效、快速地向验证者分发区块信息,最大限度地减少带宽需求,提高网络的可扩展性。考虑到Solana的高交易吞吐量和由此产生的大区块,这一点对Solana尤为重要。
该协议采用了一种独特的数据传输方法,类似于BitTorrent,即将区块分成较小的块,然后分发给一组验证者。然后,这些验证者以结构化的方式将数据传递给其他验证者,确保整个网络快速有效地接收信息。这种分散的区块传播方式降低了出现瓶颈的可能性,并确保网络在大负荷下仍能保持弹性。

Solana与其他区块链(如以太坊)的比较
目前,以太坊使用工作证明(PoW)机制(尽管将在以太坊2.0中过渡到PoS),与之相比,Solana凭借其独特的架构和共识机制,大大提高了交易速度,降低了成本。以太坊目前的TPS远低于Solana,导致交易费用较高,尤其是在网络拥堵时。Solana能够以极低的成本处理成千上万的TPS,这对追求效率和可扩展性的开发者和用户来说是一个极具吸引力的平台。
虽然以太坊拥有更大的生态系统和更发达的基础设施,但Solana正快速发展,以其高性能和低成本交易吸引着开发者。以太坊2.0的推出可能会缩小这种性能差距,但Solana的独特功能(如Gulf Stream和Sealevel)为其提供了竞争优势。安全模式也不尽相同;以太坊即将转向PoS,旨在提高能效和可扩展性,但Solana的集成PoH增加了一层额外的安全和效率,使其有别于以太坊和其他PoS区块链。
总之,尽管以太坊仍然是区块链领域的主导力量,但对于需要高吞吐量和低交易成本的应用来说,Solana以其创新的架构和共识机制为后盾,提供了一个令人信服的替代方案。
Solana是如何实现回归的?
亮点
- Solana 采用权益证明(PoS)共识机制,并通过历史证明(PoH)加以强化,实现了快速高效的交易处理,具有高吞吐量和低延迟的特点。
- Gulf Stream、Sealevel、Tower BFT 和 Turbine 等关键功能有助于提高 Solana 处理高交易量、支持并行智能合约执行以及确保网络安全和快速数据传播的能力。
- 与以太坊目前的 PoW(将在以太坊 2.0 过渡到 PoS)相比,Solana 的交易速度明显更高,成本更低,因此对开发者和用户来说是一个极具吸引力的平台。
- Solana 的架构和共识机制旨在解决区块链三难问题,同时实现可扩展性、安全性和去中心化,使其有别于其他区块链平台。
- 尽管以太坊拥有更大的生态系统,但 Solana 的性能优势和创新功能使其成为需要高效、可扩展区块链解决方案的应用程序的一个具有竞争力的替代选择。





